Anal abscess
definition
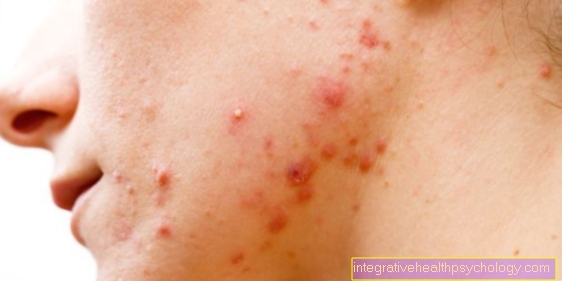
Under a Anal abscess one usually understands one pus and more inflammatory Liquid-filled cavity that is located in the area of the Afters located and mostly severe discomfort when sitting and walking.
Cause and forms of the anal abscess
In contrast to an anal fistula, an anal abscess does not create a connecting duct from the anus to other organs.
The abscess is closed and has no opening. Depending on the stage, it contains pus or inflammatory fluid, which increases in amount and causes the abscess to swell when unopened.

In which Anal abscess it is usually a disease of the Afters located Glands, which are also called Proctodeal glands are designated. Inflammation of these glands can lead to a corresponding Abscess formation to lead.
In addition, a Anal abscess in the area of the anus also result from the propagation of inflammation and diseases of internal organs. For example:
- the Appendicitis or one
- Inflammation of an unnoticed bulging of the bowel (Diverticulosis), also called Diverticulitis referred to as.
More information on the subject Anal abscess see the main article abscess.
A steady spread of this inflammation can lead to abscess formation in extreme cases. Also can inflammatory bowel disease, like Crohn's disease or Ulcerative colitis lead to such an education.
In addition to the acquired causes described here, innate Malformations of the rectum and anus to a painful Anal abscess in the area of the anus. Depending on the location of the abscess, different forms are distinguished:
- Anal abscesses located just under the skin are also called subcutaneous abscess designated.
- If the anal abscess develops between the epidermis and the mucous layer, the abscess formation is also known as submucosal abscess.
- When the anal abscess spreads between the sphincters of the anus, it is called intermuscular abscess,
- when the anal abscess spreads from the iliac bone to the anus as ischiorectal abscess designated.
- Furthermore there is pelvirectal and ileorectal Abscess courses.
Symptoms of an anal abscess
In most cases, patients who have developing anal abscesses describe moderate to severe tenderness in the area of the abscess formation, especially when sitting.
Sometimes very severe pain is described with an anal abscess when defecating. In many cases, the anal abscess can be seen and felt where it originated. If you put pressure on the swelling that has formed, severe pain is also indicated.
Please also read our article on this Pain in the rectum.
In some cases general symptoms such as deterioration in general condition or fever are described. It can also happen that the abscess opens by itself and the corresponding purulent fluid drains. The preliminary stages of complete evacuations are also described and mostly described as a chronic weeping condition.
Pain as a symptom
Acutely inflamed anal abscesses are very painful. The pain in the rectum and anus is usually accompanied by fever, fatigue, and a general feeling of illness. Due to the inflammation, the skin in the anus area is red and swollen.
When the inflammation has subsided and the pus has drained to the outside, the pain will subside for the time being. At this stage, the inflammation causes severe itching and irritation of the skin around the anus.
diagnosis
In addition to the patient survey, the physical examination represents the main part of the diagnosis of an anal abscess.
In addition to the rectal examination with the finger, reflections of the rectum can also be performed in the case of an anal abscess. It is important to differentiate whether it is an anal abscess or a fistula. The second disease would be characterized by a corresponding gait. In order to make this passage visible, either an ultrasound can be used for the examination or a color injection can be used to see whether a passage is present. In most cases, a blue paint is injected into the area around the swelling and it is seen whether the paint comes out elsewhere. This would suggest the presence of a fistula; the treatment would therefore be different from that of an anal abscess.
Which doctor is responsible for this?
To diagnose an anal abscess, the doctor examines the anus region. Doctors who specifically deal with diseases of the rectum and the anal region are known as proctologists. If an anal abscess is suspected, the family doctor can issue a referral. In the case of small abscesses, you can also contact the dermatologist.
If the abscess has to be removed surgically, a surgeon is the right contact person and responsible for further treatment.
Therapy for an anal abscess
Smaller anal abscesses can be treated with ointments that are applied to the affected area and designed to pull the contents out.
The ointments are mostly tar-containing and have the property of attracting liquids. One makes use of this in this case.
Larger anal abscesses can be punctured with a sterile needle or cannula. This leads to the mostly purulent contents being emptied and the anal abscess to shrink. In many cases, the anal abscess recurs in the same or adjacent area.
Stubborn anal abscesses and very large forms must be surgically removed in general surgery. In this case, a large area of the abscess cavity is cut out under general anesthesia. Usually the wound site is left open or only treated with a sterile wound pad. The patient is usually instructed to shower the area after using the toilet in order to prevent such infections. Wound healing after abscess surgery can be very tedious. The patient can often only sit properly after 4-6 weeks.
Read more on this topic at: Treatment of an abscess
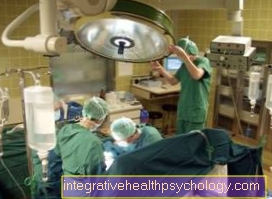
Surgery for an anal abscess

Often an operation is that only effective treatment measure in patients with anal abscess. The decision as to whether an operation is necessary depends on various factors. Consequently, the size, the location, the accompanying symptoms and the causative pathogen are particularly relevant. Especially with one large anal abscess In most cases, surgery is the only way to relieve the pain and completely remove the pus from the body.
In the case of an anal abscess, the surgical procedure is usually under general anesthetic or at least under regionally more limited Partial anesthesia carried out. During the actual operation, the attending physician cuts through the epidermis and the underlying tissue in layers. In this way, the Open abscess cavity. A large part of the purulent secretion usually drains off when it is opened. The remaining pus can then have a drainage be derived.
The biggest advantage of anal abscess surgery is the fact that the causative bacterial pathogen does not infect the surrounding area and there is no inward emptying. In this way, the risk of the bacteria entering the bloodstream and the development of one is reduced Blood poisoning minimized.
After this successfully initiated discharge of secretion the abscess cavity should be cleaned and the inflamed tissue removed during the operation. If the anal abscess is particularly large, there is a chance that it will purulent secretion again forms and another operation must be performed.
After the operation, the wound is usually treated not sewn, but a open wound healing process elected. This measure prevents any remaining liquid and bacterial pathogens from re-encapsulating each other. During the first few days after the anal abscess operation, the doctor treating the wound must have the wound cavity at regular intervals cleaned and cleaned become. In addition, the association must changed at least once a day become. Since an open wound healing method is chosen in most cases, must even after the inpatient stay a regular wound toilet should be performed. The affected patients should clean the open areas daily until the wound cavity is completely closed and also the Change associations independently. In addition, Sitz baths after successful anal abscess surgery can have a positive effect on the healing process and accelerate healing.
Although the operational opening The abscess cavity is in many cases the only effective treatment for the presence of an anal abscess certain risks get noticed. Since the OPs as a rule performed under general anesthesia there are general risks. Problems in the area of the Cardiovascular system come. In addition, during the Intubation important anatomical structures in the pharynx are injured.
In connection There is also a risk of anal abscess surgery Formation of a blood clot (thrombus) is coming. Under certain circumstances, this blood clot can loosen and vessels in the heart, lungs or brain clog. As a result, it can lead to the emergence of a Heart attack, one Pulmonary embolism or one Stroke. In addition, a patient with an anal abscess is at risk of having it even after a successful operation Wound healing disorders comes.
Laying a drain
A drain may be needed if the anal abscess cannot be completely removed during surgery or if surgery is not possible.
With the help of a guide wire, a tube is inserted into the abscess and placed. Drainage is a plastic tube through which pus and accumulated secretions can drain outwards. This will prevent the abscess cavity from becoming inflamed further.
Ointment for an anal abscess

In the case of large anal abscesses, surgical treatment is usually preferred to conservative (non-surgical) therapy. This can prevent the abscess from bursting inwards and preventing the release of bacterial pathogens into the bloodstream. In addition, after the abscess cavity has been surgically opened, a strip placed in an anti-inflammatory ointment can be placed in the wound, thereby improving the healing process. In patients who only have a small anal abscess, however, conservative treatment with the help of an ointment can be carried out for the time being. In particular, the use of ointments and / or creams that have pain relievers at their disposal is very popular with most of the affected patients.
In this context, however, it must be urgently noted that the temporary relief of the discomfort caused by the anal abscess is only due to the effectiveness of the pain reliever ointment. If their effectiveness decreases, the complaints return with the same or even increasing intensity. For this reason, a pain reliever ointment should only be used in the presence of an anal abscess to bridge the period until the next possible doctor's visit. At a immature anal abscess Surgical opening of the abscess cavity is often not useful. In such cases, treatment of the anal abscess can be done by regularly applying an antibiotic ointment. Ideally, the antibiotic ointment is applied to the anal abscess three to four times a day over a period of five to seven days.
Since in most cases an anal abscess is caused by the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus, the antibiotic ointment typically contains an active ingredient that is directed against this pathogen. However, when applying the ointment, it is essential to pay attention to hygiene. The anal abscess should never be touched with the fingers, otherwise there is a risk of the causative bacterial pathogen spreading. Ideally, the affected patients use disposable gloves when applying the ointment and then wash their hands thoroughly. In addition, the therapy of a small anal abscess can be done with the help of combination ointments. These ointments contain both pain relievers and anti-inflammatory agents. After the superficial application of the ointment, the active ingredients are absorbed through the skin and get inside the abscess cavity. After just a few applications, the symptoms caused by the anal abscess are noticeably alleviated.
In this context, however, it should be noted that even this combined ointment is not an effective method of treatment. There are also various ointments and creams that are intended to stimulate the spontaneous opening of an anal abscess. In this way, the surgical opening of the anal abscess is said to be manageable in many cases.
The best-known ointments contain active ingredients that thin the outer wall of the abscess cavity. The pressure inside the anal abscess then tends to cause a spontaneous opening that is directed outwards. However, this treatment method should be critically examined, especially in patients with a large anal abscess. Thinning the outer wall of the abscess cavity reduces the likelihood of internal emptying, but does not completely eliminate it. In the worst case, there is still a risk of the bacterial pathogens entering the bloodstream and the development of blood poisoning (sepsis).
Read more on this topic at: Treatment with ointment for an abscess
Pull ointment for the treatment of an anal abscess
Small anal abscesses do not have to be surgically removed, but can be treated with a pulling ointment. Pull ointments have an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect. The application of the pulling ointment also promotes blood circulation, so that the melting of the pus is accelerated by the body's own immune system. As a result, the abscess breaks open and the accumulated pus can drain through the skin.
Antibiotics used to treat anal abscesses
In most cases, an abscess is surgically removed. To fully combat the bacteria, antibiotic therapy is then carried out for several days. The administration of antibiotics is important because otherwise there is a risk that the inflammation will spread and lead to life-threatening blood poisoning (sepsis).
Since an abscess is an encapsulated pus cavity with poor blood supply, it is difficult for medication to reach the inflamed tissue. Therefore, the administration of antibiotics alone is not enough to treat the anal abscess effectively.
Home remedies to treat an anal abscess
In most cases, anal abscesses must be removed surgically. If you suspect an abscess or an anal fistula, you should definitely consult a doctor to discuss how to proceed. The patient can also pay attention to a few important points and use home remedies to accelerate healing.
Most importantly, under no circumstances should the abscess be squeezed out, as it can lead to dangerous infections and, in the worst case, blood poisoning.
Abscesses are caused by bacteria and occur especially in people with a weakened immune system. A strong immune system helps the body fight inflammation.
A balanced diet and plenty of exercise in the fresh air help to strengthen the immune system. Sufficient sleep and little stress promote physical well-being and help the anal abscess to heal.
An anal abscess is very painful, which is made worse by hard stools. Lots of fluids (drink enough) and a low-fiber diet help the stool take on a soft consistency. Regular exercise also stimulates the bowel movements and helps against hard stools.
Other home remedies for anal abscesses are nettle tea and chamomile tea. Nettle has an anti-inflammatory effect and the consumption of three cups of freshly brewed nettle tea a day accelerates wound healing. Compresses soaked in chamomile tea can be placed on the abscess and will help pull the pus out.
Read more on the topic: Home remedies for an abscess
Tea tree oil, used to treat an anal abscess
Tea tree oil is a popular natural remedy that consists of the essential oils of the tea tree.
Tea tree oil can be used to treat an anal abscess. A few drops of tea tree oil are placed on a damp cloth or washcloth and placed on the affected area for several hours. The tea tree oil will help fight the infection and dissolve the pus.
Tea tree oil should not be used on open wounds and will not help treat large abscesses. If in doubt, a doctor must be consulted, otherwise the infection and complications can spread.
Healing an anal abscess
How quickly an anal abscess heals depends on its size and location. In general, however, it takes a relatively long time for an anal abscess to heal completely.
The treatment method of first choice is surgical cleavage of the abscess. The skin over the inflammation is removed and the pus can drain away. This surgery is usually a routine and straightforward procedure. The removal of the inflamed tissue creates a relatively large wound that is up to several centimeters deep and that is not sutured but remains open. This will prevent a new anal abscess from forming. The wound must be carefully cleaned by the patient and the bandages changed regularly.
The surgery is followed by antibiotic therapy to completely eliminate the bacteria that caused the abscess from the body. Usually, operated anal abscesses heal completely. However, it can take a long time for the wound to close completely, and it will take several weeks for the wound to heal completely.
How well the wound heals in general depends on many factors including on age, nutritional status, previous illnesses and medication intake.
Smoking worsens the blood circulation in the body, which negatively affects wound healing. For this reason, patients should avoid nicotine after the abscess has been surgically removed in order not to delay the healing of the wound unnecessarily.
Duration of an anal abscess
The duration of an anal abscess varies from person to person and depends on various factors such as location, size of the abscess and the type of treatment. Small abscesses can usually be treated conservatively, which means that they do not have to be removed surgically, but can be treated with pulling ointment for several days.
Larger anal abscesses, however, must be surgically removed. The entire abscess cavity and the surrounding tissue are cut out. The patient has to stay in the hospital for three to four days. In the case of simple abscesses, the removal can also be done on an outpatient basis. Several weeks or even months can pass until the wound has healed completely.
What is the difference between an anal abscess and an anal fistula?
An anal abscess is an encapsulated collection of pus in a cavity caused by the inflammation near the anus. In many cases, the chronic inflammation of an anal abscess creates an anal fistula.
An anal fistula is a tubular connection between the abscess and the anal region through which the purulent secretion drains to the outside.















.jpg)